Overview
We organize files in folders for easy access. If we put all files in a single folder, it will be very difficult to locate the file that you are looking for. Similarly in Java also we have option to organize our files.
Java Packages
All classes in Java are organized in packages. Packages in Java are used for grouping related classes and sub-packages together.
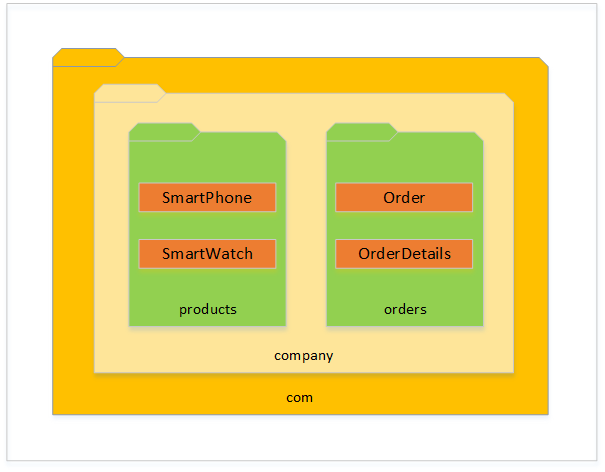
In the above package structure, SmartPhone class is placed under products package, which is present within a package called as “company”, which is again part of package “com”.
Members within a package are referred with all of its parent packages. We use import keyword to load class in another class.
import com.company.products.SmartPhoneAdvantages of using Packages
- The main advantage of packages is that it prevents confliction of classes when multiple classes with same name are to be loaded by JVM
- Packages allow us to group related classes and interfaces in relevant packages to make it clutter free
- Usage of packages will also help us to hide certain attributes using protected access specifier if you do not want them to be accessible to other packages
Using a Class Without Importing
You can refer to a class with its fully qualified name without importing. When I say fully qualified name of class, I mean class name with its package name.
In the following example, we are trying to instantiate a class without importing it.
public class Test {
public static void main(String args[]) {
java.util.ArrayList list = new java.util.ArrayList();
}
}When to use fully qualified class names?
- We’ll have to use fully qualified class names when we have multiple classes with same name.
- We are not using the class in many places
- You want to create the instance of a class using Class.forName() method
Rules for Naming a Package
- A package name should not begin with a number
- A package name cannot have special characters other than a dot, dollar and underscore symbols
- A package name cannot start or end with a dot
- The declared package name should match with the directory path of that class file (not source file, it’s optional). If you are using IDE, you don’t have to worry about this rule as this will be taken care by default and throws error if both are not matching
- If you are compiling a bunch of Java source files through command line without any defined folder structure, but with package name within source files, make sure to compile them with -d flag and specifying where you want to copy the class files
Naming Conventions of Package
Lower Case
In Java, it is a standard practice to name the package all in lower case.
Reversed Domain Name
To maintain the uniqueness of your class you can name the package with your reversed domain name or website name (excluding www) of your organization.
package com.techstackjournal;Group of Groups
You can further separate various groups within the organization to maintain the uniqueness within organization.
package com.techstackjournal.finance;